
Employee representation
Works councils are in-house committees representing the interests of the employees within a company.
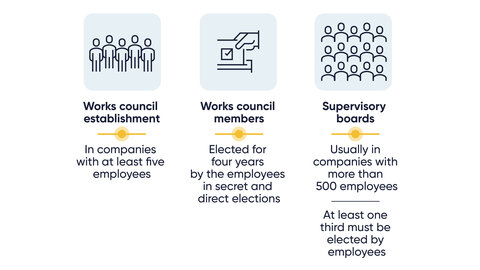
A works council may be established in companies with five or more employees. Works council members are elected for four years by the employees in direct and secret elections. Candidates do not have to be union members.
In certain companies (e.g. stock corporations or limited liabilty companies) that have more than 500 employees and a supervisory board, at least one third of the supervisory board members must be representatives elected by the employees.
Functions and rights of works councils
The rights and functions of works councils are governed by the German Works Council Constitution Act (Betriebsverfassungsgesetz). Works councils have informative and advisory rights relating to company internal policy and organization. Specifically, they can negotiate rules pertaining to organizational and social issues, and must be consulted regarding specific personnel decisions. Apart from the rights defined by statute, the works council is generally prohibited from becoming involved in corporate governance. The employer and works council can negotiate rules on matters such as:
-
end and beginning of daily working hours (not the duration as such)
-
vacation schedules
-
internal order and rules of conduct
-
safety issues (accident prevention)
-
installation of equipment designated to monitor employees
-
mobile work
-
general company wage structures (but not individual salaries)